Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The distance between Earth and the Moon was determined by measuring the time it
took for light waves from Earth to travel to the Moon and back. Why was it not possible to use
sound waves for this experiment? (MCAS 2007)
a. | Sound waves must move through a substance. | b. | Sound waves would
change frequency on the return to Earth. | c. | Sound waves move too slowly for the technique
to be accurate. | d. | Sound waves move more slowly in Earth’s atmosphere than in
space. |
|
|
|
2.
|
A sound wave can be transmitted through all of the following except ____.
(MCAS 2008)
a. | a gas | b. | a liquid | c. | a solid | d. | a
vacuum |
|
|
|
3.
|
People perceive sound differently in air than they do under water. Which of the
following correctly compares the motion of sound waves in air and in water? (MCAS 2008)
a. | Sound waves travel faster in air than in water. | b. | Sound waves travel
slower in air than in water. | c. | Sound waves travel in air but do not travel in
water. | d. | Sound waves travel at the same speed in air and in
water. |
|
|
|
4.
|
To locate objects in their environments, bats in flight and porpoises under
water both use ultrasound waves with frequencies that are beyond human hearing. These animals produce
an ultrasonic wave and then detect echoes from nearby objects. If a porpoise and a bat both produce
ultrasonic waves when they are 16 m from an object, which animal would hear its echo first and why?
(MCAS 2009)
a. | The bat would hear its echo first because sound travels faster in air than in
water. | b. | The porpoise would hear its echo first because sound travels faster in water than in
air. | c. | The bat would hear its echo first because the amplitude of sound waves is greater in
air than in water. | d. | The porpoise would hear its echo first because
the amplitude of sound waves is greater in water than in air. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following observations is a result of the Doppler effect? (MCAS 2009)
a. | Noise from across a lake is louder at night than during the day. | b. | A person walking
notices that the pitch of a car’s engine decreases as the car passes by. | c. | Beats are produced
when two tuning forks with different frequencies are heard together. | d. | A person hears the
sound from a radio more clearly in certain areas of a room than in
others. |
|
|
|
6.
|
The source of a sound is moving away from an observer who is standing still. How
do the sound waves received by the observer compare with those emitted by the source? (MCAS 2010)
a. | They are heard as having a greater velocity. | b. | They are heard as
having a higher frequency. | c. | They are heard as having a lower
frequency. | d. | They are heard as having a smaller wavelength. |
|
|
|
7.
|
When a student listens to music, sound waves propagate from the speaker to her
ear. Which of the following is a physical description of this process? (MCAS 2010)
a. | Particles produced at the speaker move to the student’s
ear. | b. | Energy is transported from the speaker to the student’s
ear. | c. | Material is transferred from the speaker to the student’s
ear. | d. | Clusters of air molecules are sent from the speaker to the student’s
ear. |
|
|
|
8.
|
A star suddenly explodes. Which of the following types of waves reach
Earth’s surface? (MCAS 2010)
a. | light only | c. | sound followed by light | b. | sound
only | d. | light followed by
sound |
|
|
|
9.
|
A loud buzzer is swinging like a pendulum. An observer is near one end of the
buzzer’s path, as shown below. 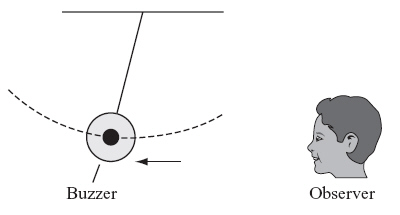 Which of the following describes
and explains what the observer hears as the buzzer moves away from him? (MCAS 2011)a. | a lower-pitched buzz than the buzzer’s normal sound because the sound waves are
arriving less frequently | b. | a higher-pitched buzz than the buzzer’s
normal sound because the sound waves are arriving more frequently | c. | a lower-pitched buzz
than the buzzer’s normal sound because the velocity of the sound waves is reduced by the
velocity of the swinging buzzer | d. | a higher-pitched buzz than the buzzer’s
normal sound because the velocity of the sound waves is increased by the velocity of the swinging
buzzer |
|
|
|
10.
|
A car with its horn sounding approaches a group of students. Assume the
car’s horn produces sound waves with a constant frequency. Which of the following statements
best explains why the students hear a higher pitch as the car approaches than when it is
stopped? (MCAS 2011)
a. | The sound waves increase in speed as the car approaches the
students. | b. | The sound waves decrease in speed as the car approaches the
students. | c. | The sound waves are heard at a lower frequency as the car approaches the
students. | d. | The sound waves are heard at a higher frequency as the car approaches the
students. |
|
|
|
11.
|
A person creates a longitudinal wave by shouting into a tube in the direction
indicated by the arrow on the diagram below. The dot inside the tube represents an air particle in
the tube before the wave reaches it. 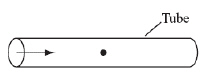 Which of the following diagrams best
represents the motion of the air particle when the wave travels through the tube? (MCAS 2011)
|
|
|
12.
|
The picture below shows a sound speaker in a cabinet with its front panel
removed. 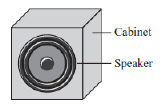 When music plays through the speaker, the speaker
rapidly moves back and forth in the cabinet. Which of the following conclusions is best
supported by this observation? (MCAS 2012)a. | Sound travels only in air. | c. | Sound is a longitudinal
wave. | b. | Sound is a transverse wave. | d. | Sound travels at the speed of light. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The siren of a fire truck emits a certain pitch, which is heard by a nearby
observer. In which of the following situations would the observer perceive the lowest frequency of
sound? (MCAS 2012)
a. | The observer and fire truck are both stationary. | b. | The observer walks
at 3 m/s toward the stationary fire truck. | c. | The observer is stationary while the fire truck
drives toward the observer at 15 m/s. | d. | The observer is stationary while the fire truck
drives away from the observer at 15 m/s. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Student X and student Y are receiving sound waves from a stationary source. The
sound waves have a frequency of 10 kHz. Student X is stationary and student Y is traveling toward the
source of the sound waves. Which of the following statements describes what will happen as student Y
moves? (MCAS 2012)
a. | Student X will receive sound waves with a frequency higher than 10
kHz. | b. | Student X will receive sound waves with a frequency lower than 10
kHz. | c. | Student Y will receive sound waves with a frequency higher than 10
kHz. | d. | Student Y will receive sound waves with a frequency lower than 10
kHz. |
|
|
|
15.
|
In which of the following media do sound waves most likely travel the
fastest? (MCAS 2012)
a. | crude oil | b. | distilled water | c. | solid steel | d. | warm
air |
|
|
|
16.
|
A person is driving north in a car at a constant speed. A police officer is
driving south toward him at a constant speed. The police officer uses a radar unit to measure the
speed of the person’s car. The radar unit sends out waves of a certain frequency toward the
person’s car. The waves reflect off the person’s car and travel back to the radar unit in
the police car. What happens to the frequency of the waves detected by the radar unit? (MCAS 2013)
a. | The frequency is lower as the person’s car approaches. | b. | The frequency is
higher as the person’s car approaches. | c. | The frequency remains the same but with
increased energy as the person’s car approaches. | d. | The frequency remains the same but with
decreased energy as the person’s car approaches. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following observed properties of a wave is changed by the Doppler
effect? (MCAS 2013)
a. | amplitude | b. | direction | c. | frequency | d. | speed |
|
|
|
18.
|
Sound travels through air, steel, and water at different speeds. Which list is
ordered from the substance that sound will travel through the slowest to the substance that sound
will travel through the fastest? (MCAS 2013)
a. | air, water, steel | b. | steel, air, water | c. | water, air, steel | d. | water, steel,
air |
|
|
|
19.
|
A loud alarm attached to a metal fence begins to ring. Student X has her ear
against a pole of the fence while student Y stands away from the fence, as shown below. Both students
are the same distance from the alarm. 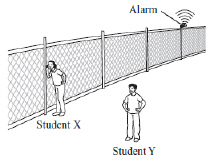 Which of the following statements
explains what happens in this situation? (MCAS 2014)a. | Student X hears the alarm first because sound travels faster in solids than in
gases. | b. | Student X hears the alarm at a higher pitch because solids are denser than
gases. | c. | Student Y hears the alarm first because sound travels faster in gases than in
solids. | d. | Student Y hears the alarm at a higher pitch because gases are denser than
solids. |
|
|
|
20.
|
A student conducted two investigations using a toy car and microphones, as shown
below. 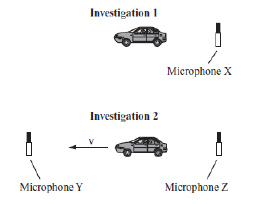 The toy car contained a buzzer. The microphones
were used to record the frequency of sound. In investigation 1, the buzzer frequency was measured
while the toy car was at rest. In investigation 2, the toy car was in motion and the observed
frequency was measured in front of and behind the car. Which of the following graphs represents the
frequency recorded by each microphone? (MCAS 2014)
|
Essay
|
|
|
21.
|
Rita and John stand at opposite ends of a long section of steel track from an
abandoned railroad line. Rita places a penny on her end of the track. John then strikes his end of
the track with a rock. (MCAS 2009)a. Describe what Rita sees happen to the
penny on the track and explain her observation. Rita puts her ear on the track. John strikes his end
of the track with the rock again.
b. Describe the difference in
speed between the sound Rita hears in the air and the sound she hears through the track.
c.
With the rock, John strikes his end of the track harder than before.
Identify which sound wave property he has changed.
|
|
|
22.
|
A large anchor is being lifted into a boat with metal sides. As the anchor
leaves the water it hits the side of the boat, making loud sounds and making waves on the surface of
the water. (MCAS 2011)a.
Describe the motions of the sound waves and the water waves.
b.
Draw a diagram for each of the waves you described in part (a).
Be sure to label each diagram.
c. Describe how the wavelength is
measured for the water waves.
|