Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
What property of electromagnetic waves makes it possible to use these waves to
transmit information between a space shuttle and NASA mission control centers on the ground? (MCAS 2004)
a. | Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. | b. | Electromagnetic
waves have very low velocity. | c. | Electromagnetic waves are all visible to human
eyes. | d. | Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following is designed to transform an electromagnetic wave into a
mechanical wave? (MCAS 2004)
a. | a portable radio | c. | a computer monitor | b. | a television screen | d. | a mercury
thermometer |
|
|
|
3.
|
A plastic filter is fitted over a light. The light emits white light, but the
filter only lets the longest wavelengths of visible light pass through. Which color would a person
looking at the filtered light see? (Modified MCAS 2004)
a. | green | b. | red | c. | violet | d. | yellow |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which of the following describes how a microwave oven heats food? (MCAS 2005)
a. | The oven’s interior reflects heat onto the food. | b. | The oven’s
interior, like a lens, focuses heat onto the food. | c. | Water molecules in the food reflect energy from
microwave radiation. | d. | Water molecules in the food absorb the energy
of microwave radiation. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The figure below shows regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. 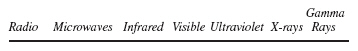 Which of the following waves has the highest frequency? (MCAS 2005)a. | visible light | b. | microwaves | c. | ultraviolet rays | d. | infrared
radiation |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following best describes the relationship between frequency
and wavelength of electromagnetic waves? (MCAS 2005)
a. | If the frequency remains constant, the wavelength increases. | b. | The wavelength
decreases as the frequency decreases. | c. | The frequency increases as the wavelength
decreases. | d. | If the wavelength remains constant, the frequency
increases. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is a similarity between x-ray waves and sound waves?
(MCAS 2005)
a. | Both transfer energy. | c. | Both have the same speed. | b. | Both require a
vacuum. | d. | Both have the same
frequency. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The figure below shows regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. 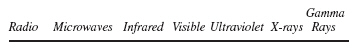 Which of the following statements
best compares the wavelengths of the regions of the
electromagnetic spectrum? (MCAS 2006)a. | Microwaves are shorter than x-rays. | b. | Infrared waves are longer than gamma
rays. | c. | Radio waves are shorter than visible light waves. | d. | Ultraviolet waves
are longer than visible light waves. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following colors of visible light
has the longest wavelength? (MCAS 2006) a. | red | b. | blue | c. | green | d. | orange |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following devices relies on electromagnetic radiation in the radio
wave region of the spectrum for operation? (MCAS 2006)
a. | sun tanning lamp | c. | cellular telephone | b. | electric light bulb | d. | electric
toaster |
|
|
|
11.
|
Visible light passes through glass. Other types of electromagnetic radiation are
able to pass through other materials in a similar way. Which of the following are used in medical
technology because they can pass through some parts of the human body? (MCAS 2006)
a. | x-rays | b. | infrared waves | c. | microwaves | d. | ultraviolet
rays |
|
|
|
12.
|
Some campers are sitting around a campfire outside their tent. Which product of
the fire is in the form of electromagnetic waves? (MCAS
2006)
a. | light | b. | smoke | c. | sound | d. | water
vapor |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following can carry light waves but not sound waves? (MCAS 2007)
a. | air | b. | steel | c. | water | d. | vacuum |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following waves can travel at a speed of 3 x 108 m/s?
(MCAS 2007)
a. | microwaves | b. | seismic waves | c. | ultrasonic waves | d. | water waves
|
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship of the
frequency of an electromagnetic wave to its wavelength? (MCAS
2007)
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following waves travels fastest? (MCAS 2007)
a. | water waves in oceans | c. | sound waves from a violin string | b. | seismic waves in
rocks | d. | electromagnetic waves
from the Sun |
|
|
|
17.
|
Ultraviolet light has a shorter wavelength than visible light. Which of the
following is another way ultraviolet light can be compared to visible light? (MCAS 2007)
a. | Ultraviolet light has a lower frequency than visible light. | b. | Ultraviolet light
has a higher frequency than visible light. | c. | Ultraviolet light travels faster than visible
light. | d. | Ultraviolet light travels slower than visible light. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following waves travels fastest? (MCAS 2007)
a. | water waves in oceans | c. | sound waves from a violin string | b. | seismic waves in
rocks | d. | electromagnetic waves
from the Sun |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is possible due to longitudinal waves? (MCAS 2008)
a. | seeing the color red | c. | hearing the sound of the ocean | b. | getting a tan at the
beach | d. | riding a wave on a
surfboard |
|
|
|
20.
|
Radio waves, visible light, and x-rays are examples of electromagnetic waves
that always differ from each other in ____. (MCAS
2008)
a. | amplitude | b. | intensity | c. | temperature | d. | wavelength |
|
|
|
21.
|
X-ray waves and infrared waves are both electromagnetic waves. Which of the
following describes another property x-ray waves and infrared waves share? (MCAS 2008)
a. | Both waves are longitudinal. | b. | Both waves have the same
frequency. | c. | Both waves have the same wavelength. | d. | Both waves travel at the same speed in a
vacuum. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Suppose a scientist detects an electromagnetic wave with a frequency higher than
those of gamma rays. The scientist labels this wave a Z-ray. Which of the following would always be
true of a Z-ray? (MCAS 2008)
a. | A Z-ray would have a lesser amplitude than gamma rays. | b. | A Z-ray would have a
greater amplitude than gamma rays. | c. | A Z-ray would have a shorter wavelength than
gamma rays. | d. | A Z-ray would have a longer wavelength than gamma
rays. |
|
|
|
23.
|
A student is sitting in a large stadium far away from the starting line of a
footrace, while listening to the footrace on the radio. As the race starts, the student hears the
sound of the starting pistol on the radio. Shortly after that, the student hears the sound of the
starting pistol from inside the stadium. Which of the following best explains these observations?
(MCAS 2008)
a. | Mechanical waves travel faster than electromagnetic waves. | b. | Electromagnetic
waves travel faster than mechanical waves. | c. | The radio’s signal traveled a shorter
distance than the sound wave traveled. | d. | The radio’s microphone was farther away
from the starting line than the student was. |
|
|
|
24.
|
A student standing on the edge of a swimming pool sees a painted mark on the
bottom of the pool. The mark appears to be at a shallower depth than the actual depth of the pool.
Which of the following descriptions of light waves best explains this observation? (MCAS 2008)
a. | Light from the mark travels through the water in a curved path. | b. | Light from the mark
is refracted as it travels from the water to the air. | c. | Light from the mark is reflected as it travels
from the water to the air. | d. | Light from the mark bounces off the boundary
between the water and the air. |
|
|
|
25.
|
The diagram below shows a light ray striking a plane mirror surface at an angle
of 40° to the normal. 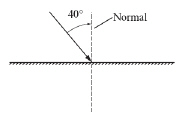 Which of the following diagrams shows the
ray that is reflected from the plane mirror surface? (MCAS
2009)
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following statements best describes the visible spectrum of
light as seen by the human eye? (MCAS 2009)
a. | The lowest frequency appears red, and the highest frequency appears
violet. | b. | The lowest frequency appears red, and the highest frequency appears
yellow. | c. | The lowest frequency appears green, and the highest frequency appears
violet. | d. | The lowest frequency appears green, and the highest frequency appears
yellow. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Electromagnetic waves of various frequencies reach Earth from distant parts of
the universe. Which of the following can be inferred from this? (MCAS
2009)
a. | The wavelengths must be very short. | b. | A single material must fill all of
space. | c. | These waves can travel without a medium. | d. | The speed of these
waves is 300,000,000 m/s. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following statements best describes an electromagnetic wave with a
long wavelength? (MCAS 2009)
a. | It has a low frequency and can travel in a vacuum. | b. | It has a high
frequency and can travel in a vacuum. | c. | It has a low frequency and can only travel in a
medium. | d. | It has a high frequency and can only travel in a
medium. |
|
|
|
29.
|
In an electromagnetic wave, an electric field exists perpendicular to a magnetic
field, and both fields are perpendicular to the direction of travel of the wave. These
characteristics indicate that an electromagnetic wave is which of the following wave types? (MCAS 2009)
a. | gravitational | b. | longitudinal | c. | mechanical | d. | transverse |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is an example of an electromagnetic wave? (MCAS 2009)
a. | a radio wave | c. | the oscillation of a spring | b. | a water
wave | d. | the vibration of a
violin string |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following properties is the same for all electromagnetic waves in a
vacuum? (MCAS 2010)
a. | amplitude | b. | frequency | c. | speed | d. | wavelength |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following properties determines a color in the visible light region
of the electromagnetic spectrum? (MCAS 2010)
a. | acceleration | b. | amplitude | c. | frequency | d. | speed |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following is designed to produce an electromagnetic wave? (MCAS 2010)
a. | elastic cord | b. | laser pointer | c. | metal spring | d. | ripple
tank |
|
|
|
34.
|
The diagram below shows a light ray striking the flat surface of a piece of
clear hard plastic at an angle of 45°. Light travels faster in air than through plastic. 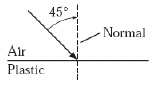 Which of the following diagrams shows how the ray is refracted after it travels
through the plastic? (MCAS 2010)
|
|
|
35.
|
The table below lists the speed of light in four different situations. 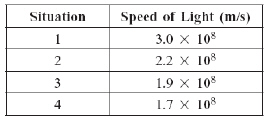 In which situation is light traveling through a vacuum? (MCAS 2011)a. | situation 1 | b. | situation 2 | c. | situation 3 | d. | situation
4 |
|
|
|
36.
|
The diagram below shows an incident light ray striking a shiny piece of aluminum
foil. 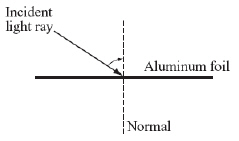 Which of the following statements
describes what will most likely happen to the light ray after it strikes the aluminum foil?
(MCAS 2011)a. | The light ray will be absorbed by the shiny metal. | b. | The light ray will
be refracted after passing through the shiny metal. | c. | The light ray will be reflected at a different
angle to the normal than the incident light ray. | d. | The light ray will be reflected at the same
angle to the normal as the incident light ray. |
|
|
|
37.
|
The figure below shows regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.  Which of the following devices is designed to produce electromagnetic radiation with
the longest wavelength in order to operate? (MCAS
2011)a. | light bulb | c. | x-ray microscope | b. | microwave oven | d. | FM radio
transmitter |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following observations demonstrates that visible light waves are
electromagnetic and not mechanical? (MCAS 2011)
a. | Sunlight can pass through gas. | c. | Sunlight can pass through
liquids. | b. | Sunlight can pass through solids. | d. | Sunlight can pass through a
vacuum. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following statements best explains why lightning is seen
before thunder is heard? (MCAS 2011)
a. | Electromagnetic waves travel faster than mechanical waves in air. | b. | Electromagnetic
waves have a higher frequency than mechanical waves. | c. | Electromagnetic waves experience less
interference than mechanical waves. | d. | Electromagnetic waves form faster than
mechanical waves during a thunderstorm. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following statements best describes a difference between
mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves? (MCAS 2012)
a. | Mechanical waves can produce colored light, while electromagnetic waves
cannot. | b. | Mechanical waves can travel in any direction, while electromagnetic waves travel only
in one direction. | c. | Mechanical waves travel only through a medium,
while electromagnetic waves can also travel through a vacuum. | d. | Mechanical waves
travel only at the speed of light, while electromagnetic waves can travel at many different
speeds. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the following statements explains why light is refracted as it moves
from air into glass? (MCAS 2012)
a. | The speed of light decreases in glass. | b. | The energy of light increases in
glass. | c. | The frequency of light decreases in glass. | d. | The wavelength of
light increases in glass. |
|
|
|
42.
|
Ultraviolet and x-ray radiation can damage human cells. Which of the following
is a property of these two forms of radiation? (MCAS 2012)
a. | low wave speed | c. | low wave frequency | b. | short wavelength | d. | small wave
amplitude |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following best represents an electromagnetic wave? (MCAS 2012)
|
|
|
44.
|
Electromagnetic waves with low frequencies have been used for long-distance
underwater communication. These waves most likely belong to which of the following parts of
the electromagnetic spectrum? (MCAS 2013)
a. | gamma rays | b. | infrared waves | c. | radio waves | d. | x-rays |
|
|
|
45.
|
During a thunderstorm, which of the following travels at a speed closest to
3.00 ´ 108 m/s? (MCAS 2013)
a. | wind from the storm | c. | light from the lightning | b. | sound from the
thunder | d. | rain from the storm
clouds |
|
|
|
46.
|
Which of the following properties makes a light wave different from all
mechanical waves? (MCAS 2013)
a. | A light wave slows down in a vacuum. | b. | A light wave is able to transmit
energy. | c. | A light wave exists as a transverse wave. | d. | A light wave can
travel without a medium. |
|
|
|
47.
|
Which of the following always occurs when a light ray reflects off a mirror?
(MCAS 2013)
a. | The speed of the light ray increases. | b. | The direction of the light ray stays the
same. | c. | The frequency of the light ray decreases as it reflects and loses energy to the
mirror. | d. | The angle at which the light ray strikes the mirror equals the angle at which it
reflects. |
|
|
|
48.
|
Sunscreen protects skin by absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
Ultraviolet radiation has which of the following properties? (MCAS
2014)
a. | a shorter wavelength than x-rays | c. | a higher frequency than visible
light | b. | a lower frequency than radio waves | d. | a longer wavelength than
microwaves |
|
|
|
49.
|
A small object is placed in a room with a narrow mirror on the wall. Four
positions in the room are labeled W, X, Y, and Z, as shown below. 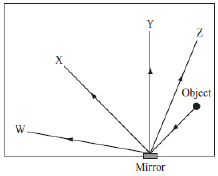 At which
position should a person stand to see the reflection of the object in the mirror? (MCAS 2014)a. | position W | b. | position X | c. | position Y | d. | position
Z |
|
|
|
50.
|
The picture below shows what a straight pipe looks like in a container of water
when viewed from the side. 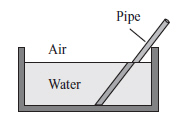 What is happening in this example as light
travels from the water into the air? (MCAS 2014)a. | absorption | b. | diffraction | c. | reflection | d. | refraction |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the following is a difference between electromagnetic waves and
mechanical waves? (MCAS 2014)
a. | Electromagnetic waves transmit energy, and mechanical waves transmit
information. | b. | Electromagnetic waves are always longitudinal, and mechanical waves are always
transverse. | c. | Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, and mechanical waves require a
medium. | d. | Electromagnetic waves have only low frequencies, and mechanical waves have only high
frequencies. |
|
|
|
52.
|
Grains and spices are irradiated with gamma rays to kill most of the bacteria or
fungi that are normally present. Although microwaves are another form of radiation, the properties of
these waves do not make them as useful as gamma rays for sterilizing food. In which of the following
ways do gamma rays differ from microwaves? (MCAS 2014)
a. | Gamma rays have a lower frequency and longer wavelength than
microwaves. | b. | Gamma rays have a lower frequency and shorter wavelength than
microwaves. | c. | Gamma rays have a higher frequency and longer wavelength than
microwaves. | d. | Gamma rays have a higher frequency and shorter wavelength than
microwaves. |
|
Open-Response Questions
- BE
SURE TO ANSWER AND LABEL ALL PARTS OF THE QUESTION. - Show all your work (diagrams,
tables, or computations).
- If you do the work in your head, explain in writing how you did the
work.
|
|
|
53.
|
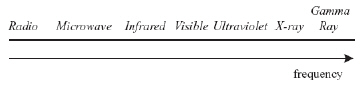
The electromagnetic spectrum is shown below.
(MCAS 2006)
 There are multiple stages involved in the transmission, reception, and
display of a television broadcast. A signal is sent by satellite from the station and relayed to the
television by several methods. The signal is translated electronically and converted into an image on
regular, liquid crystal, or plasma TV displays. The viewer then sees the image.
a. Identify one region of the
electromagnetic spectrum used by television and explain how it is used.
b.
Select a different portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is
not used by television. Explain a useful application of this spectral region.
|
|
|
54.
|
The diagram below shows what happens when a particular light wave strikes a
boundary. (MCAS 2008)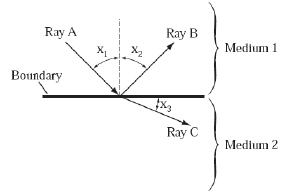 a. Identify each light ray, A, B, and C, as
an incident, a refracted, or a reflected ray.
b. Describe the
relationship between angles x1 and
x2.
c. Describe how this setup could be changed so
that the size of angle x3 is different.
|
|
|
55.
|
When some elements are put into a flame, they emit colored light. Yellow light
is emitted from one element and violet light is emitted from another element. (MCAS 2010)
a.
Describe the differences between yellow light and violet light in
terms of frequency and wavelength. The diagram below represents violet light. 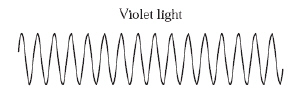 b. Draw and label a representation of yellow light that
illustrates how its frequency and wavelength are different from that of violet light. c.
Yellow light and violet light are both in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Identify
two other similarities between yellow light and violet light.
|
|
|
56.
|
When fireworks explode, they create light waves and sound waves. An
investigation is performed to study the differences between the two types of waves. Three cameras
capable of recording audio and video are set up at safe nearby locations in clear view of the
fireworks. (MCAS 2012)•
Camera 1 is placed in an open field.
• Camera 2 is placed in a vacuum-sealed
glass container.
• Camera 3 is placed behind
sheets of polarizing glass that block electromagnetic waves.
a. Identify whether audio only, video only, or both audio and video of the
fireworks will be recorded by each camera.
b. Explain each of your answers for part
(a).
Suppose a camera records both audio and
video.
c. Will the light or the sound from the fireworks be
recorded first? Explain your answer.
|
|
|
57.
|
The diagram below is a simplified representation of the inside of a certain type
of camera. (Modified MCAS 2013)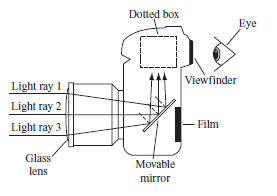 a.
Identify and describe the wave behavior as the light rays pass through the glass
lens. b. Identify and describe the wave behavior as the light rays strike the
mirror. c. In the dotted box, draw what must happen inside the
box for light ray 2 to strike the viewfinder. Be sure to include the following:
• either a lens or a
mirror that is labeled
• the path of light ray
2
• a line normal to the surface where light ray 2
strikes
|
|
|
58.
|
Waves can be classified as either electromagnetic
or mechanical.
a. Describe two differences between electromagnetic and mechanical
waves. b. Give two examples of electromagnetic waves. c. Give two examples of
mechanical waves.
|