Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following is the best example of a wave? (MCAS 2004)
a. | a stone rolling downhill | b. | a vehicle traveling on a bumpy
road | c. | a string vibrating on a guitar | d. | a grasshopper jumping up and down
occasionally |
|
|
|
2.
|
The diagram below shows a wave trace. (MCAS
2004)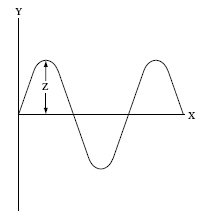 Distance Z is a measure of a. | amplitude. | b. | frequency. | c. | wavelength. | d. | wave
speed. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Each of the following illustrations shows the movement of a 1 kg object. Which
of these is an example of simple harmonic motion? (MCAS
2005)
|
|
|
4.
|
An organ pipe produces a musical note with a wavelength of 2.72 m. What is
the frequency of this note if the speed of sound is 348 m/s? (MCAS
2005)
a. | 85.7 Hz | b. | 128 Hz | c. | 260 Hz | d. | 466
Hz |
|
|
|
5.
|
Five bowling balls are lined up touching one another on a smooth surface.
Striking the first ball with a hammer makes the fifth ball move away from the group. The force of the
hammer was transmitted through the line of balls as what type of wave? (MCAS 2005)
a. | electromagnetic | b. | heat | c. | longitudinal | d. | transverse |
|
|
|
6.
|
The diagram below represents a mass suspended vertically by a rubber band. The
mass is set in motion by pulling down slightly on the mass and letting go. 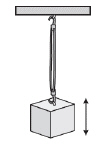 Which of the following correctly identifies the up-and-down motion of the mass? (MCAS 2006)a. | torsional | b. | transverse | c. | nonharmonic | d. | simple
harmonic |
|
|
|
7.
|
The illustration below shows three toy ducks floating on water, moving up and
down as a wave travels to the right with a velocity of 3 m/s. (MCAS
2006)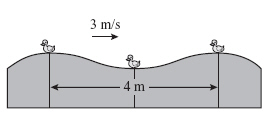 Which of the following is the frequency of
the wave? a. | 0.75 Hz | b. | 1.33 Hz | c. | 1.5 Hz | d. | 6.0
Hz |
|
|
|
8.
|
The figure below shows a spring with a wave traveling through it. (MCAS 2006)
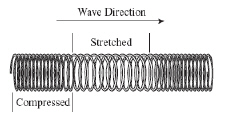 Which type of wave is
illustrated? a. | sound | b. | transverse | c. | longitudinal | d. | electromagnetic |
|
|
|
9.
|
What is the frequency of ocean waves that have a
speed of 18 m/s and a wavelength of 50 m? (MCAS 2006) a. | 0.18 Hz | b. | 0.36 Hz | c. | 2.8 Hz | d. | 9.0 Hz
|
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following provides the best
example of simple harmonic motion? (MCAS 2007) a. | riding a regular bus route | c. | running a consistent daily
jog | b. | sliding down a water slide | d. | swinging on a playground swing |
|
|
|
11.
|
The diagram below shows a wave generator that emits a wave with a frequency of
500 Hz and a wavelength of 0.1 m. (MCAS 2007)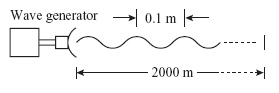 How long does it take for the wave to travel a distance of 2000 m?
|
|
|
12.
|
The illustration below shows wave traces of recorded sound waves on two computer
screens. (MCAS 2007)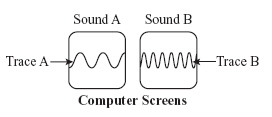 Traces A
and B represent two different sounds with the same time scale horizontally. From a comparison of the
wave traces, which of the following correctly describes the relationship of sound B to sound
A? a. | Sound B has a higher velocity. | c. | Sound B has a higher
frequency. | b. | Sound B has a higher amplitude. | d. | Sound B has a longer
wavelength. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following waves travels fastest? (MCAS 2007)
a. | water waves in oceans | c. | sound waves from a violin string | b. | seismic waves in
rocks | d. | electromagnetic waves
from the Sun |
|
|
|
14.
|
The diagram below shows a hammer about to strike
a moveable piston. (MCAS 2007)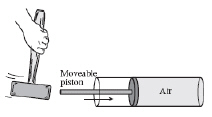 As the
piston moves suddenly when struck, which type of wave pulse is generated in the air inside the
cylinder? a. | electromagnetic | b. | transverse | c. | refracted | d. | longitudinal |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following statements applies to a longitudinal wave? (MCAS 2008)
a. | The motion of the medium is random. | b. | The motion of the medium is in a circular
pattern. | c. | The motion of the medium is parallel to the motion of the wave. | d. | The motion of the
medium is perpendicular to the motion of the wave. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Two students stretch a rope horizontally between them. One student moves one end
of the rope up and down repeatedly for a short time. Which of the following describes the frequency
of the waves in the rope? (MCAS 2008)
a. | the height that the rope reaches when moved up | b. | the amount of time
it takes for one wave to travel the length of the rope | c. | the number of times the rope is moved up and
down in a time interval | d. | the distance measured between the crest of one
wave and the crest of the next wave in the rope |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is possible due to longitudinal waves? (MCAS 2008)
a. | seeing the color red | c. | hearing the sound of the ocean | b. | getting a tan at the
beach | d. | riding a wave on a
surfboard |
|
|
|
18.
|
A boat tied to a dock is stationary. Water waves constantly pass by the boat.
The crests of the waves are 3 m apart and a crest passes the front of the boat every 4 s. What is the
velocity of the waves? (MCAS 2008)
a. | 0.75 m/s | b. | 1.33 m/s | c. | 3 m/s | d. | 12
m/s |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is an example of a nonharmonic motion? (MCAS 2009)
a. | particles colliding with one another | b. | a pendulum swaying back and
forth | c. | a child bouncing up and down on a large spring | d. | waves created on the
surface of a glass of water during an earthquake |
|
|
|
20.
|
A large spring is stretched horizontally between two people. One person wiggles
the spring up and down at one end. The up-and-down vibration then moves along the spring to the other
person. Which of the following types of wave is created in the spring? (MCAS 2009)
a. | pressure wave | c. | longitudinal wave | b. | transverse wave | d. | nonmechanical
wave |
|
|
|
21.
|
The speed of sound in a particular gas is 900 m/s. A sound wave propagating in
this material has a wavelength of 15 m. What is the frequency of this sound? (MCAS 2009)
a. | 30 Hz | b. | 60 Hz | c. | 6,800 Hz | d. | 13,500
Hz |
|
|
|
22.
|
The graphs below give information for waves W and X. Both waves were produced in
the same medium and are moving at the same speed. 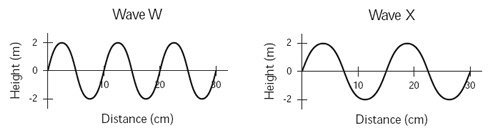 Which of the following
statements describes another property of these waves? (MCAS
2010)a. | Wave W has a larger period than wave X. | b. | Wave W has a lower
frequency than wave X. | c. | Wave W has a greater amplitude than wave
X. | d. | Wave W has a shorter wavelength than wave X. |
|
|
|
23.
|
A teacher asks a group of students to use a ruler to measure the amplitude of
the wave shown below. 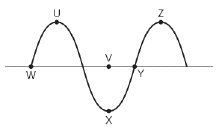 Between which of the following points
should the amplitude be measured? (MCAS 2010)a. | points U and Z | b. | points V and X | c. | points W and Y | d. | points X and
Z |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following would cause a change in the speed of a mechanical wave?
(MCAS 2010)
a. | the wave moving through a liquid | b. | the wave moving from a solid to a
gas | c. | the wave being made by a larger vibration | d. | the wave being made
by a smaller vibration |
|
|
|
25.
|
A string is tied on a spring. Two students then stretch out the spring, as shown
below. 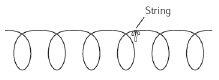 In which of the following ways does the
string move when the students generate a longitudinal wave in the spring? (MCAS 2010)
|
|
|
26.
|
The diagram below shows a wave with four numbered parts. 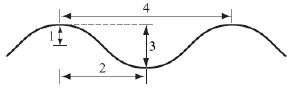 Which numbered part of the diagram represents the wavelength? (MCAS 2011)
|
|
|
27.
|
In a large room, a sound wave traveling from a violin produces a tone with a
frequency of 264 Hz. The speed of sound in the room is 340 m/s. What is the wavelength of the sound
wave from the violin? (MCAS 2011)
a. | 0.004 m | b. | 0.80 m | c. | 1.3 m | d. | 2.6
m |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following diagrams represents the refraction of waves? (MCAS 2011)
|
|
|
29.
|
A student is sitting on the edge of a swimming pool. The student repeatedly dips
his foot in and out of the pool, making waves that move across the water. The student dips his foot
slowly at first and then does it faster, each time to the same depth. Which of the following
properties of the waves increases as the student dips his foot faster? (MCAS 2012)
a. | frequency | b. | period | c. | velocity | d. | wavelength |
|
|
|
30.
|
A rope is stretched horizontally between two students. One of the students
shakes an end of the rope up and down. Which of the following terms best describes the type of
wave that is produced? (MCAS 2012)
a. | electromagnetic | b. | longitudinal | c. | rotational | d. | transverse |
|
|
|
31.
|
Two waves traveling in the same medium are shown below. 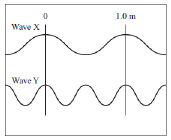 Which of the following correctly compares the two waves? (MCAS 2012)a. | Wave X has half the amplitude of wave Y. | b. | Wave X has twice the
amplitude of wave Y. | c. | Wave X has a lower frequency and longer
wavelength than wave Y. | d. | Wave X has a higher frequency and shorter
wavelength than wave Y. |
|
|
|
32.
|
A 2 m long pendulum swings back and forth 6 times in 17 seconds. What is the
period of the pendulum? (MCAS 2013)
a. | 0.4 s | b. | 2.8 s | c. | 12 s | d. | 34
s |
|
|
|
33.
|
A student is shaking one end of a small rug with a ball on top of it. The wave
that is produced travels through the rug and moves the ball upward, as shown in the diagram below.
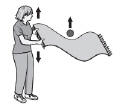 Which type of wave is produced in the rug?
(MCAS 2013)a. | compression | b. | electromagnetic | c. | longitudinal | d. | transverse |
|
|
|
34.
|
The diagram below shows two students making a wave with a coiled spring.
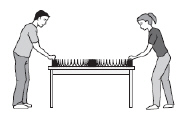 Which of the following waves move most
like the wave in the coiled spring? (MCAS 2013)a. | infrared waves | c. | sound waves | b. | microwaves | d. | ultraviolet
waves |
|
|
|
35.
|
Waves rock a boat in the middle of a pond. The boat moves up and down 10 times
in 20 s.
What is the period of the waves? (MCAS 2014)
|
|
|
36.
|
A sound wave with a frequency of 1,700 Hz is traveling through air at a speed of
340 m/s. What is the wavelength of this sound wave? (MCAS
2014)
a. | 0.2 m | b. | 5.0 m | c. | 2,040 m | d. | 57,800
m |
|
|
|
37.
|
The diagram below shows a representation of two different waves. 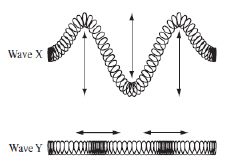 Which of the following classifies wave X and wave Y? (MCAS
2014)a. | Both waves are transverse. | b. | Both waves are
longitudinal. | c. | Wave X is longitudinal and wave Y is transverse. | d. | Wave X is transverse
and wave Y is longitudinal. |
|
Open-Response questions.
BE SURE TO ANSWER AND LABEL ALL PARTS OF
EACH QUESTION.
Show all your work (diagrams, tables, or computations).
If you do the
work in your head, explain in writing how you did the work.
|
|
|
38.
|
The drawing below shows two students holding the ends of a spring that has a
ribbon attached to it. (MCAS 2007)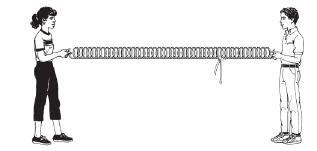 a. Draw and explain how a
transverse wave will move along the spring.
b. Draw and explain
how the ribbon will move when a transverse wave is sent along the spring.
c.
Draw and explain how a longitudinal wave will move along the spring.
d. Draw and explain how the ribbon will move when a longitudinal
wave is sent along the spring.
|
|
|
39.
|
A large anchor is being lifted into a boat with metal sides. As the anchor
leaves the water it hits the side of the boat, making loud sounds and making waves on the surface of
the water. (MCAS 2011)a.
Describe the motions of the sound waves and the water waves.
b.
Draw a diagram for each of the waves you described in part (a).
Be sure to label each diagram.
c. Describe how the wavelength is
measured for the water waves.
|