Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A heavy box is at rest on an inclined plane. The box begins to slide down the
inclined plane when a small force is applied to the box. The force is removed as soon as the box
begins to slide. The speed of the box increases as the box slides down the inclined plane.
Which
of the following is the most likely cause of this increasing speed? (MCAS 2008)
a. | The force of gravity on the box is less when the box is not moving than when the box
is moving. | b. | The force of gravity on the box is greater when the box is not moving than when the
box is moving. | c. | The force of friction on the box is less when the box is not moving than when the box
is moving. | d. | The force of friction on the box is greater when the box is not moving than when the
box is moving. |
|
|
|
2.
|
An engineering student is gathering data on the motion of a model car traveling
down a ramp. If energy is conserved, the potential energy of the car at the top of the ramp should
equal the kinetic energy of the car at the bottom of the ramp. After the first trial, the student
calculates that the kinetic energy at the bottom of the ramp is less than the potential energy at the
top of the ramp. Which of the following can best explain this difference? (MCAS 2008)
a. | The car gained a small amount of mass as it moved down the ramp. | b. | The student
accidentally accelerated the car at the top of the ramp. | c. | The measured height
of the ramp was less than the actual height. | d. | The student did not include the effect of
frictional force in the calculation. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following is a scalar quantity? (MCAS
2008)
a. | the mass of a brick | b. | the velocity of a falling tennis
ball | c. | the force required to lift a 10 kg mass | d. | the acceleration of
a toy car over a 60 s period |
|
|
|
4.
|
A car is parked on the side of a hill. Which of the following most likely
prevents the car from moving down the hill? (MCAS 2007)
a. | The car has too much mass to move easily. | b. | There is friction in
the door hinges of the car. | c. | There is friction between the tires and the
road. | d. | The weight of the car is mostly on the front wheels. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following is a vector quantity? (MCAS
2007)
a. | mass | c. | temperature | b. | force | d. | kinetic energy |
|
|
|
6.
|
The forces acting on a skateboarder moving at a constant velocity along a
sidewalk are shown in the figure below. 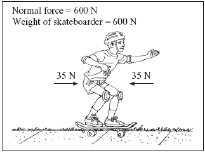 Which of the following
is the net force on the skateboarder? (MCAS 2006)a. | 0 N | c. | 670 N | b. | 70 N | d. | 1270 N |
|
|
|
7.
|
An upward force of 150 N is applied to a box weighing 70 N. Which of the
following is the free-body force diagram for this situation? (MCAS
2006)
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following must be included
with magnitude to represent a vector? (MCAS 2006) a. | mass | c. | acceleration | b. | direction | d. | volume |
|
|
|
9.
|
The diagram below shows the forces acting on a rock. 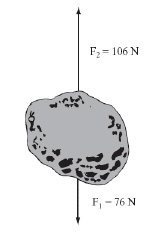 The weight of the rock is 76 N. An upward force of 106 N is exerted on the rock. What
is the net force acting on the rock? (MCAS 2009)a. | 30 N upward | c. | 106 N upward | b. | 76 N downward | d. | 182 N downward |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following is an example of a vector quantity? (MCAS 2009)
a. | A student walks 2.0 km north. | b. | An object has a mass of 10.5
kg. | c. | A 1.0 kg object moves at 18 m/s. | d. | A ball has an instantaneous speed of 15
m/s. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following statements best explains why it is usually easier
to keep a sliding object moving than it is to start the object moving? (MCAS 2009)
a. | Kinetic friction is typically equal to static friction. | b. | Kinetic friction is
typically less than static friction. | c. | Kinetic friction is a force that resists
attempts to start an object moving. | d. | Kinetic friction is a force that opposes the
sliding of two objects over each other. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The illustration below shows a 2-ton elephant balancing on a tree stump.
 Which of the following statements must be
accurate? (MCAS 2005)a. | The weight of the tree stump is greater than 2 tons. | b. | A 4-ton force on the
ground spreads out in all directions. | c. | The tree stump is exerting a 2-ton force upward
on the elephant. | d. | The downward force on the ground under the tree stump is 4
tons. |
|
|
|
13.
|
A hot air balloon exerts a force of 1200 N while
lifting a load of 800 N. Which free-body force diagram depicts the forces involved? (MCAS 2005)
|
|
|
14.
|
Two forces act on the 2 kg box shown below. 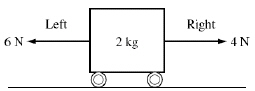 A 4 N
force acts to the right and a 6 N force acts to the left. What is the net force acting on the box?
(MCAS 2004)a. | 10 N to the right | c. | 2 N to the right | b. | 10 N to the left | d. | 2 N to the left |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following arrangements will
remain stationary unless an external force acts on it? Assume there is no friction. (MCAS 2004)
|
|
|
16.
|
Four students push on a block of wood with the forces shown in the diagram
below. Assume friction is negligible. (MCAS 2010)The block slides horizontally. What
is the net force acting on the block of wood? a. | 3 N to the left | c. | 11 N to the right | b. | 8 N to the left | d. | 25 N to the
right |
|
|
|
17.
|
A 2000 kg car is pulling a 1000 kg trailer. The car’s engine exerts a 6000
N force to move the car and the trailer. In addition, the car and the trailer each experience a 1000
N frictional force as they are being pulled, as represented below. What is the magnitude of the net
force on this system? (MCAS 2010)a. | 2000 N | c. | 5000 N | b. | 4000 N | d. | 8000 N |
|
|
|
18.
|
A student pushes a book across a classroom table. Which of the following
statements best explains the difference between the amount of force needed to start the book
moving and the amount of force needed to keep it moving? (MCAS
2011)
a. | Less force is needed to start the book moving, because there is less friction than
when it is already moving. | b. | Less force is needed to start the book moving,
because there is less potential energy in the table than in the book. | c. | More force is needed
to start the book moving, because there is more potential energy in the table than in the
book. | d. | More force is needed to start the book moving, because there is more friction than
when it is already moving. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following statements identifies the main difference between vector
and scalar quantities? (MCAS 2011)
a. | Only vectors have direction. | b. | Only scalars have
magnitude. | c. | Only scalars have units associated with them. | d. | Only vectors have
units associated with them. |
|
|
|
20.
|
A person pushes a heavy cabinet across a level wooden floor. Force X is the
force required to start the cabinet moving. Force Y is the force required to maintain a slow, steady
forward motion. Which of the following statements describes the two forces, X and Y? (MCAS 2012)
a. | Force X is added to force Y. | c. | Force X is unrelated to force
Y. | b. | Force X is less than force Y. | d. | Force X is greater than force
Y. |
|
|
|
21.
|
A crate is being pulled along a floor by means of two ropes. A frictional force
opposes the motion of the crate. The diagram below shows these three forces acting on the
crate. 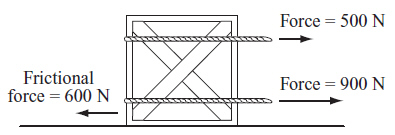 What is the magnitude of the net force
acting on the crate? (MCAS 2012)a. | 800 N | c. | 1400 N | b. | 1000 N | d. | 2000 N |
|
|
|
22.
|
A car is moving at 25 m/s north. Which of the following is a vector
quantity? (MCAS 2012)
a. | the speed of the car | c. | the potential energy of the car | b. | the velocity of the
car | d. | the distance traveled
by the car |
|
|
|
23.
|
A rope is attached to a block that has a weight of 120 N. When the rope exerts
an upward force of 250 N on the block, what is the net force on the block? (MCAS 2013)
a. | 130 N up | c. | 130 N down | b. | 370 N up | d. | 370 N down |
|
|
|
24.
|
The diagram below represents a block sliding across a table at a constant speed.
All forces are shown except the frictional force. 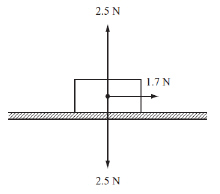 What is
the magnitude of the frictional force on the block? (MCAS
2013)a. | 0.8 N | c. | 1.7 N | b. | 1.6 N | d. | 2.5 N |
|
|
|
25.
|
The graph below illustrates the motion of a toy car during time intervals X, Y,
and Z. The toy car is initially at rest. It is then pushed and released. 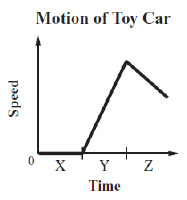 Kinetic friction is acting on the toy car during which of the following time
intervals? (MCAS 2013)a. | interval X only | c. | intervals X and Z | b. | interval Y only | d. | intervals Y and
Z |
|
|
|
26.
|
A toy cart that has a weight of 10 N moves with a constant velocity of 2 m/s to
the right on a horizontal table. According to Newton’s laws of motion, which of the following
statements is correct? (MCAS 2009)
a. | The table exerts a force of 10 N upward on the toy cart. | b. | The toy cart exerts
a force of 10 N upward on the table. | c. | The toy cart exerts a force of 2 N downward on
the table. | d. | The table exerts a force of 2 N to the right on the toy
cart. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following examples includes a vector quantity? (MCAS 2014)
a. | a 10.0 kg object | c. | a 3.5 kg object moving at 1.5 m/s | b. | a truck that
traveled 12.5 m | d. | a car
moving northeast at 90 km/hr |
|
|
|
28.
|
A car is parked on a flat driveway. Which of the following is a free-body
diagram for this car? (MCAS 2014)
|
|
|
29.
|
The free-body diagram below represents all the forces acting on an object.
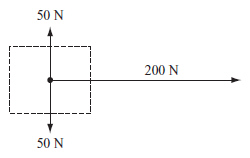 What is the net force acting on this
object? (MCAS 2014)a. | 0 N up | c. | 200 N right | b. | 100 N down | d. | 300 N right |
|
|
|
30.
|
A toy truck powered by a battery is accelerating to the right. A string with
negligible mass is attached to the truck. The diagram below shows the forces acting on the truck.
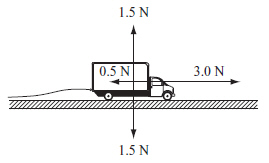 If a child pulls the string to the left,
what force must the child exert to make the toy truck move to the right at a constant velocity? (MCAS 2014)a. | 1.0 N | c. | 2.5 N | b. | 1.5 N | d. | 6.0 N |
|
|
|
31.
|
A person pushes a couch across a wooden floor. What force changes when the couch
first begins to move? (MCAS 2014)
a. | frictional force | c. | normal force | b. | gravitational force | d. | tension force |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following is an example of an object that could have a net force
greater than zero acting on it? (MCAS 2014)
a. | a glass resting on a table | b. | a ball rolling down a ramp | c. | a ladder leaning
against a wall | d. | a toy car moving east at a constant velocity |
|
Essay
|
|
|
33.
|
An elastic cord made for bungee jumping is being tested. A weight of 800 N is
attached to one end of the bungee cord. Then the weight is released from a tall tower and it moves
downward. When the elastic cord is fully extended, it exerts an opposing force of 900 N on the
weight. (MCAS 2008)a.
Draw and label a force diagram for this situation.
b.
Calculate the net force on the weight. Show your calculations and
include units in your answer.
c. Explain what would happen if
the elastic cord exerted a maximum force of only 700 N on the weight.
|
|
|
34.
|
A student is conducting experiments with a block of wood. In experiment 1, the
student pulls the block of wood with a constant force of 10 N along a horizontal surface. In
experiment 2, the student pulls the same block of wood with a constant force of 10 N. The type of
surface is different from that used in experiment 1. The results of experiments 1 and 2 are shown
below. (MCAS 2010)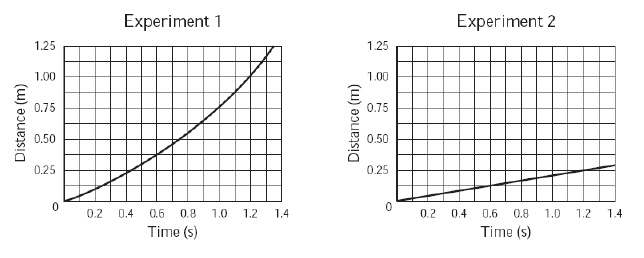 a. Using information from the graphs, compare the surface in experiment 2
with the surface in experiment 1.
b. Determine both the magnitude of the force of friction and
the net force on the block that are required to achieve the results shown in the graph for
experiment 2. Include units in your answer.
c. Without changing the type of surface used when
pulling the block of wood, list one other change to experiment 1 that would produce the results of
experiment 2. Explain your reasoning with reference to the frictional force.
|
|
|
35.
|
A 30.0 N force is continuously applied to the right on a 12.0 kg object. The
object accelerates on a horizontal frictionless surface. After a certain amount of time, another
force of 8.0 N is applied to the left on the object. (MCAS
2012)a. Calculate the object’s acceleration before
the 8.0 N force is applied. Show your calculations and include units in your answer.
b.
Calculate the object’s acceleration after the 8.0 N force is applied. Show your
calculations and include units in your answer.
c. Is the direction of acceleration in parts (a)
and (b) the same or different? Explain your answer.
The
object is then pushed onto a slightly rough surface that exerts an additional 20 N frictional force
to the left on the object.
d. Will the object come to rest on
the slightly rough surface? Explain your answer.
|
|
|
36.
|
A book is on a table. A student pushes it for a
short time. Initially the book moves, but then it comes to a complete stop. (MCAS 2007)
a.
Identify the forces acting on the book before it is pushed. You may
include a labeled diagram in your answer.
b. Explain why the
book moves and then comes to a complete stop. Use the laws of physics in your answer.
c.
The student wants the book to move at a constant speed in one
direction. Describe the physical conditions needed for this to occur.
|
|
|
37.
|
A 10 N force is applied to a 6 kg box, as shown
below. (MCAS 2014)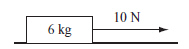 Assume the system is
frictionless. a. Determine the weight of the box in newtons. Show your calculations and
include units in your answer. b. In your Student Answer Booklet, draw a force diagram for the
box. Include labels and represent the relative magnitude of each force. c. Determine the
acceleration of the box. Show your calculations and include units in your answer. Now assume friction is introduced into the system.
d. Describe one
change to this system that would allow it to achieve the same acceleration as the frictionless
system.
|