Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Why does a plastic rod have a negative charge
after being rubbed with a piece of fur? (MCAS 2006) a. | The fur gives up protons to the rod. | c. | The fur gains protons from the
rod. | b. | The rod gives up electrons to the air. | d. | The rod gains electrons from the
fur. |
|
|
|
2.
|
A negatively charged rubber rod was brought near some small pieces of
paper. The rod’s charges repelled the negative charges in the pieces. Which of the following
caused the repulsion of the negative charges? (MCAS 2006)
a. | conduction | b. | gravitation | c. | induction | d. | insulation |
|
|
|
3.
|
The figure below shows a neutral glass rod and a
positively charged metal sphere. (MCAS 2006)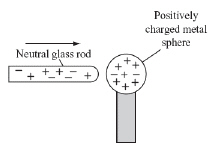 Which of the following best describes the movement of charges as this glass rod
touches the sphere? a. | Negative charges move from the sphere to the glass rod. | b. | Negative charges
move from the glass rod to the sphere. | c. | Positive charges move from the sphere to the
glass rod. | d. | Positive charges move from the glass rod to the
sphere. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Two oppositely charged objects are separated by a small distance. The objects
are then moved three times farther apart from each other. Which of the following statements best
describes what happens to the electrical force between the objects? (MCAS
2008)
a. | The force of attraction increases. | c. | The force of attraction becomes
zero. | b. | The force of attraction decreases. | d. | The force of attraction stays the
same. |
|
|
|
5.
|
A teenager removes the plastic wrapping from a CD. The pieces of wrap cling to
her hand.
Which of the following forces causes the wrap to cling to her hand? (MCAS 2008)
a. | electrostatic | b. | gravitational | c. | magnetic | d. | net |
|
|
|
6.
|
The distance between two charges is represented by d. In which of the following
diagrams is the attractive force between the two charges the greatest? (MCAS 2008)
|
|
|
7.
|
The diagram below shows two aluminum spheres.
(MCAS 2004)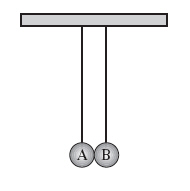 Aluminum sphere A
contains a small negative charge and is touched by aluminum sphere B, which has a larger negative
charge. Which of the following occurs next? a. | Protons flow from sphere B to sphere A. | c. | Electrons flow from sphere B to
sphere A. | b. | Protons flow from sphere A to sphere B. | d. | Electrons flow from sphere A to sphere
B. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following describes an object that must have a net negative
charge? (MCAS 2005)
a. | It contains more molecules than atoms. | c. | It is carrying an electric
current. | b. | It contains more electrons than protons. | d. | It is made of
metal. |
|
|
|
9.
|
A student combs her hair with a hard rubber comb and then hangs the comb on a
loop of light thread that is suspended from a hook as shown below. (MCAS
2005)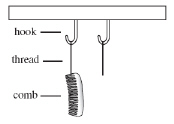 She immediately combs her hair with a
second identical comb and hangs it on the second suspended loop of light thread. If the combing has
caused a charge to accumulate on the combs, which of the following shows what will occur?
|
|
|
10.
|
A balloon is rubbed against a sweater. Which of the following occurs because of
the rubbing? (MCAS 2009)
a. | destruction of charged particles on the balloon | b. | release of charged
particles from the air in the balloon | c. | movement of negatively charged particles from
one material to the other | d. | movement of positively charged particles from
one material to the other |
|
|
|
11.
|
An electrostatic paint sprayer is used to spray paint evenly onto the surface of
a car. Before the paint is sprayed, the car body is given a positive charge and the paint droplets
are given a negative charge. The paint droplets experience an attractive force as soon as they are
released from the sprayer. The paint droplets are originally sprayed at a distance of 30 cm from the
car body, as shown below. (MCAS 2009) Which of the following changes will cause the largest increase in the
attractive force on the paint droplets? a. | The charge on the car body is doubled. | b. | The charge on the paint droplets is
doubled. | c. | The distance between the paint droplets and the car body is
halved. | d. | The distance between the paint droplets and the car body is
doubled. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following conditions results in the buildup of static charge on an
object? (MCAS 2010)
a. | when neutrons outnumber electrons | b. | when there are more protons than
neutrons | c. | when there are more electrons than protons | d. | when all neutrons
have been removed from the object |
|
|
|
13.
|
A copper sphere, a glass sphere, a plastic sphere, and a rubber sphere are
placed on individual insulating stands. A student touches each sphere with an electrically charged
object.
The sphere made of which material will distribute the electric charge fastest over its
entire surface area? (MCAS 2010)
a. | copper | b. | glass | c. | plastic | d. | rubber |
|
|
|
14.
|
In a television set with a cathode ray tube display, a beam of negatively
charged particles called cathode rays passes by a positively charged plate. The beam is deflected
before it hits the television screen to produce an image. Which of the following changes would result
in the greatest increase in the attraction between the negatively charged particles in the
beam and the positively charged plate? (MCAS 2010)
a. | increasing distance between the plate and particles and increasing the charge on the
plate | b. | increasing distance between the plate and particles and decreasing the charge on the
plate | c. | decreasing distance between the plate and particles and increasing the charge on the
plate | d. | decreasing distance between the plate and particles and decreasing the charge on the
plate |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following statements describes the electric force between two
oppositely charged particles as they approach each other? (MCAS
2011)
a. | The attractive electric force increases. | b. | The electric force
becomes repulsive. | c. | The magnitude of the electric force
decreases. | d. | The repulsive electric force becomes attractive. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Electric charges can move most easily on which of the following objects? (MCAS 2011)
a. | glass tubes | b. | metal plates | c. | plastic cups | d. | rubber
tires |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following actions would increase the electric force between two
positively charged particles? (MCAS 2012)
a. | decreasing the mass of the particles | b. | decreasing the distance between the
particles | c. | changing the charges from positive to negative | d. | transferring all the
charge from one particle to the other |
|
|
|
18.
|
A student rubs a glass rod with a piece of cloth and rubs a plastic ruler with a
different piece of cloth. The glass rod becomes positively charged, and the ruler becomes negatively
charged.
Which of the following statements describes the most likely result when the two
pieces of cloth are brought close to each other? (MCAS
2012)
a. | The pieces of cloth repel each other. | b. | The pieces of cloth attract each
other. | c. | A continuous current flows between the pieces of cloth. | d. | There is no electric
interaction between the pieces of cloth. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The diagram below shows the inside of a Van de Graaff generator. 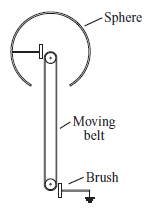 A net charge can be built up on the generator’s sphere. A moving belt removes
charged particles from the sphere and deposits them on the brush. Charged particles flow freely over
the surface of the sphere, but do not move on the belt. The generator could be made from which of the
following? (MCAS 2012)a. | a copper belt and a plastic sphere | c. | a copper belt and an aluminum
sphere | b. | a rubber belt and a plastic sphere | d. | a rubber belt and an aluminum
sphere |
|
|
|
20.
|
A neutral balloon is rubbed with a piece of wool cloth. As a result, the balloon
has a negative static charge. Which of the following statements best explains why the balloon
has a negative charge? (MCAS 2013)
a. | The balloon is a conductor. | b. | The balloon is an
insulator. | c. | The balloon transfers charges to the cloth. | d. | The balloon receives
charges from the cloth. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following graphs best represents how the force between two
identical electric charges varies as the charges move away from each other? (MCAS 2013)
|
|
|
22.
|
Two positively charged objects are separated by a large distance. One of the
positively charged objects is replaced by a negatively charged object, and the two objects are moved
closer to each other. Which of the following occurs in this situation? (MCAS 2013)
a. | The attractive force becomes a repulsive force, which increases as the objects move
closer to each other. | b. | The repulsive force becomes an attractive
force, which increases as the objects move closer to each other. | c. | The attractive force
becomes a repulsive force, which decreases as the objects move closer to each
other. | d. | The repulsive force becomes an attractive force, which decreases as the objects move
closer to each other. |
|
|
|
23.
|
What will happen when two objects with opposite electric charges are moved
closer together? (MCAS 2014)
a. | The objects will attract each other with a greater force. | b. | The objects will
attract each other with a smaller force. | c. | The objects will repel each other with a
greater force. | d. | The objects will repel each other with a smaller
force. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Electrostatic air cleaners installed in hospitals use static electricity to
reduce dust particles in the air. The neutral dust particles are attracted to positively charged ions
sprayed into the air cleaners. (MCAS 2014)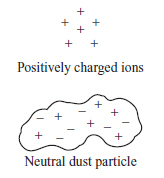
Which of the following figures shows the charge distribution on the dust particle as it is
attracted to the positively charged ions?
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following placements of two charges results in the greatest
repulsive force? (MCAS 2014)
|
Open Response
|
|
|
26.
|
A student rubs a balloon on her hair and the
balloon acquires a negative charge. (MCAS 2007)
a. Explain why the balloon acquires a
negative charge.
b. After the balloon is rubbed on the
student’s head, the student’s hair stands out from her head. Explain why this happens.
The student then brings the negatively charged balloon
near another balloon that was charged in the same way.
c. Describe and explain
what happens when the negatively charged balloon is brought near another negatively charged
balloon.
|
|
|
27.
|
In the diagram below, shaded circles 1, 2, and 3 represent fixed charged
objects, and circle 4 represents a charged object that is free to move. The magnitude of all the
charges is equal. (MCAS 2009)a.
Describe how charged objects 1, 2, and 3 will each affect
object 4.
b. Compare the magnitude of the electric force between
object 3 and object 4 with the magnitude of the electric force between object 2 and object 4.
c.
Draw a diagram to show where object 4 will most likely move in
relation to fixed objects 1, 2, and 3. Explain your answer.
|